While recording real-time data in Excel, it is hard to keep track of values and dodge duplicates. Due to this, you would have to find duplicates and de-duplicate them later which is an additional workload.
But, what if I tell you there’s a way to prevent duplicate entries?
Yes! Here, I have mentioned a technique to prompt Excel to send you a “Duplicate warning” pop-up whenever you attempt to input the repeated information. This way, you can have only unique items in your spreadsheet.
Apart from that, you can find 3 more ways to stop the same data entry in this article.
Use Data Validation
When we speak of Data Validation, we tend to immediately think of the Drop-down lists in Excel.
But, did you know that you could create a Warning Message using it?
Here’s how you can add an Error Warning and avoid duplicate entries in your sheet. On the COUNTIF formula, change your cell references as required.
- Select the Cell Range or Entire Column.
- From the Data tab, select Data Validation.
- On the window, be on the Settings tab. Set the Allow to Custom. Then, enter this formula
=COUNTIF($C:$C, C3)=1. It’ll count the duplicate entries.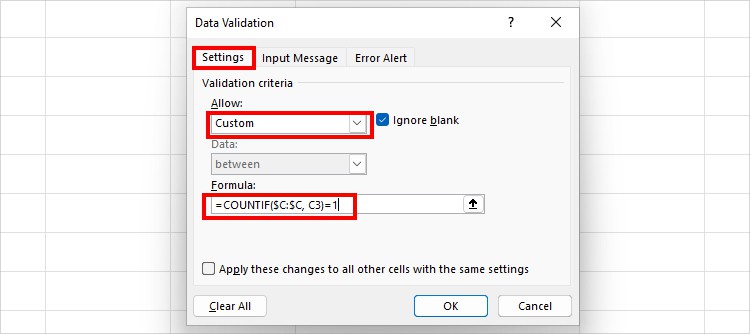
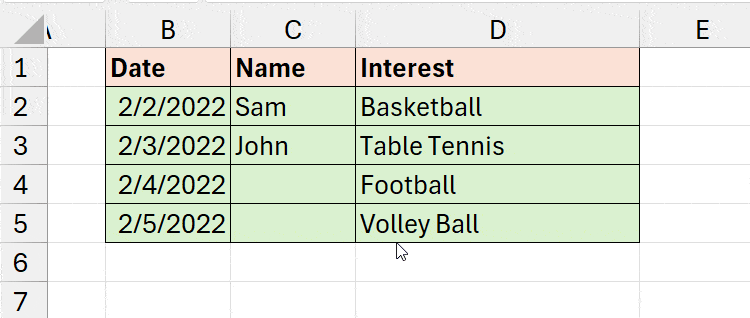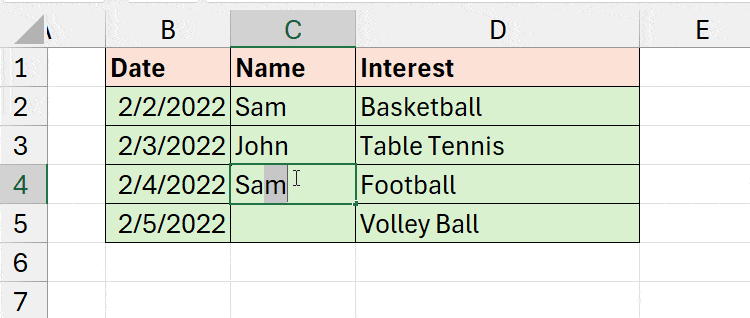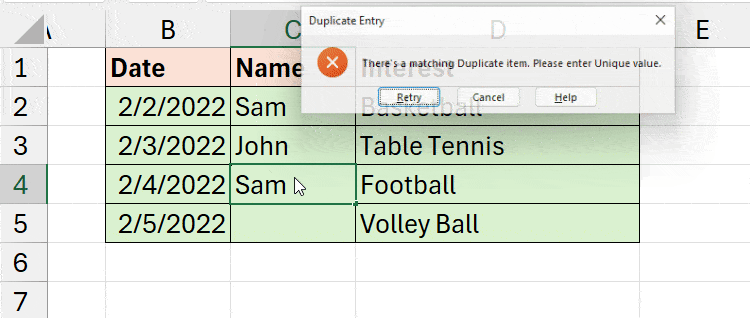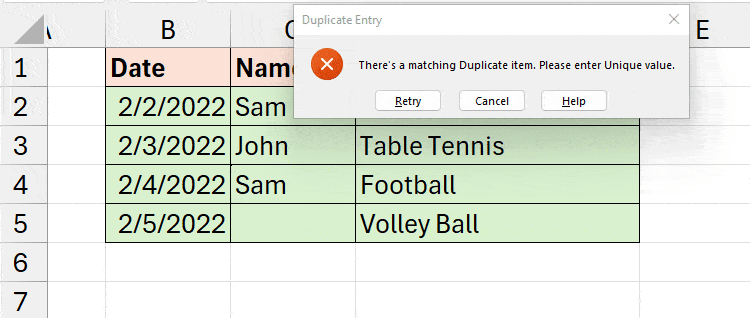
- Now, go to the Error Alert Tab. Then, fill in the Title and Error message field. For Instance, my Title is “Duplicate Entry” and Error message is “There’s a matching Duplicate item. Please enter Unique value.”
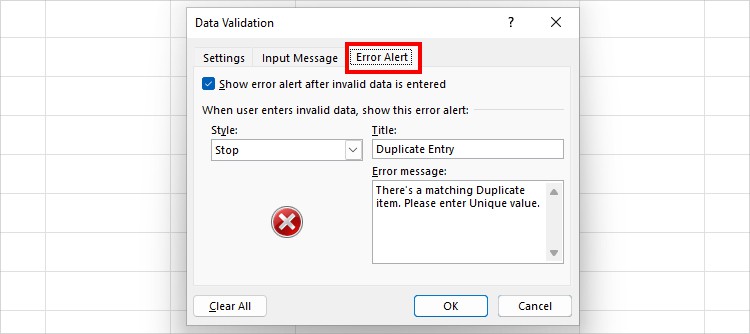
- Click OK.
To check, let’s try recording some repeated items. As soon as you type and press enter, you’ll get the “Duplicate Entry” warning we set earlier.
Use Conditional Formatting
Next, if you don’t want the error message, you could use Conditional Formatting to highlight the duplicates instead.
In this method, you can easily identify the first and repeated occurrences. So, you can choose to intentionally keep up the occurrences or omit them when required.
Here we will be using the Conditional Formatting rule prior to data entry.
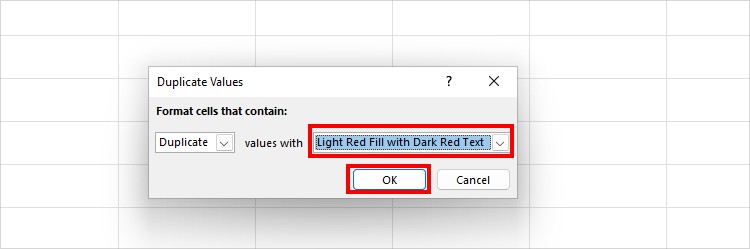
Select the empty ranges on your spreadsheet. From the Home tab, click on Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cell Rules > Duplicate Values.
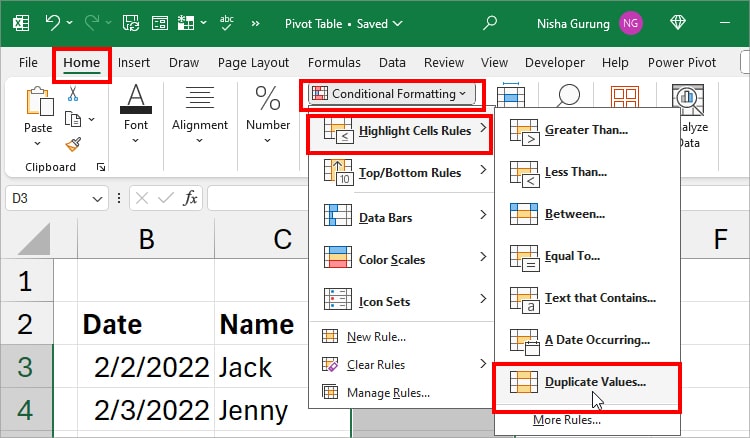
On the Duplicate Values window, pick a Colour and click OK.
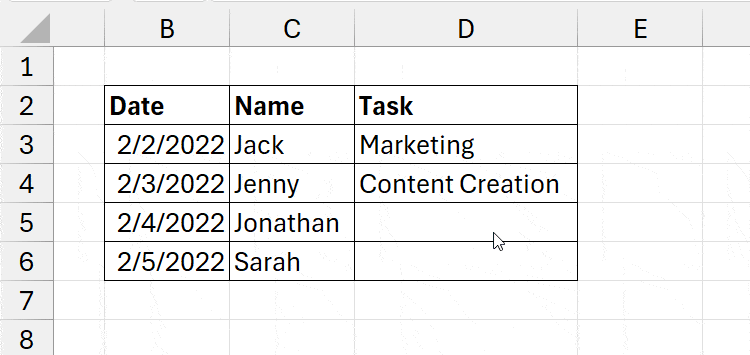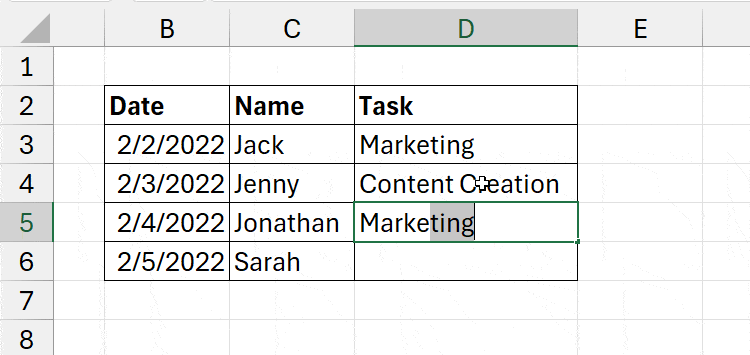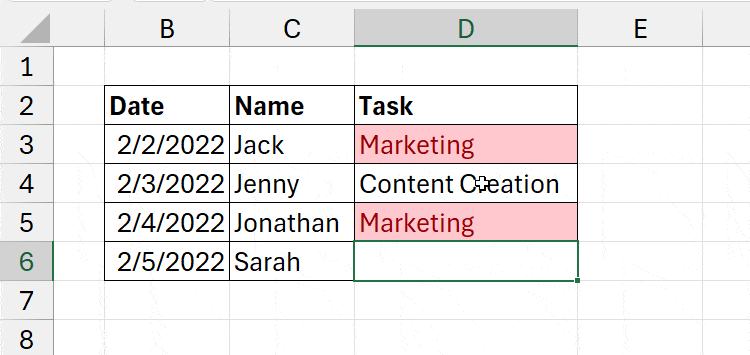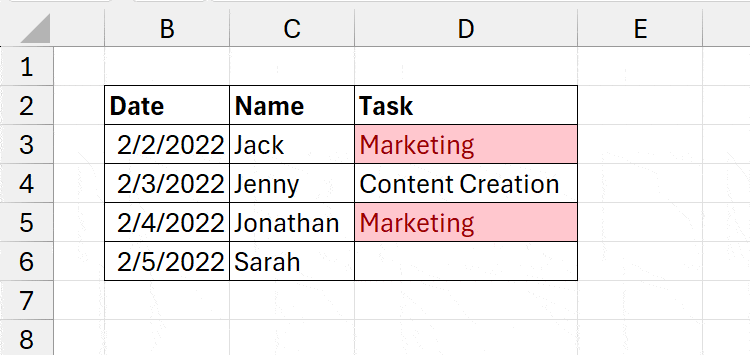
Now, if you input the same items twice or more, Excel identifies them as duplicate values and highlights the cell with the color.
Use Power Query
Let us consider that you are importing an external file and want to skip loading duplicates.
Since we use the Power Query to import most files like .TXT, .XML, .JSON, .PDF, etc, we can remove duplicates in this tool itself.
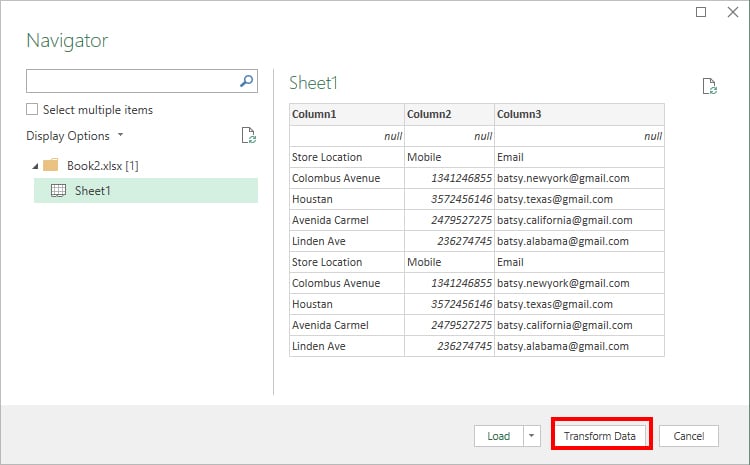
Once you’ve selected the File in the Browse window, click Transform data in the Navigator window.
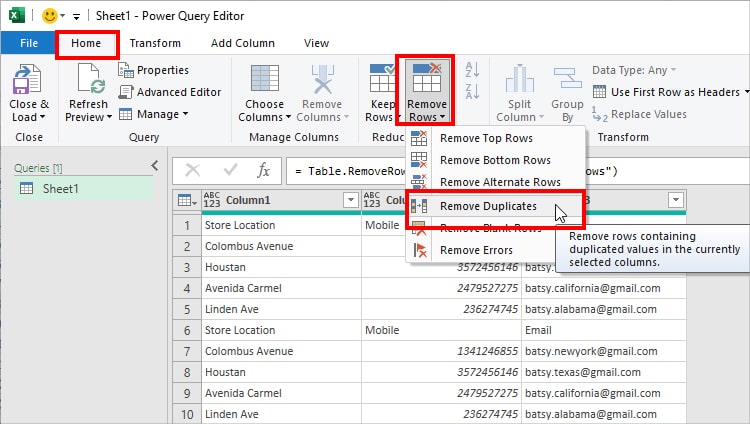
Now, in Power Query Editor, go to the Home Tab. Click on Remove Rows – Remove Duplicates.
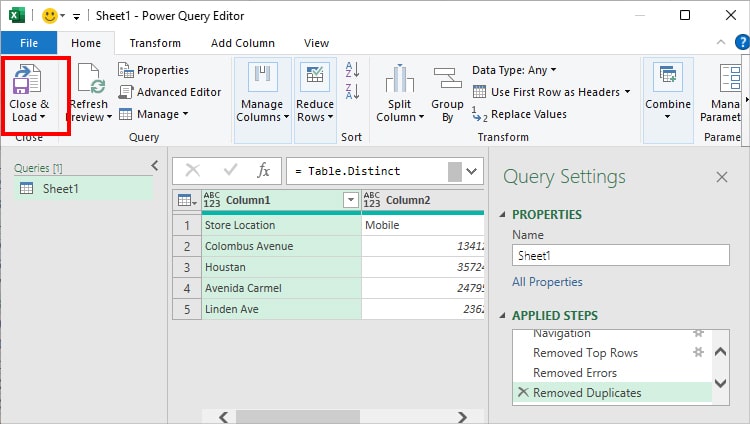
By doing so, your Data will be free of duplicates. To load data, select Close & Load.
Use VBA
Excel’s VBA, although advanced, is the best tool to execute regular tasks. Once you have the Macro, the Run button is all you need to accomplish your work within a snap. This includes preventing duplicates too.
Here, I have several VBA codes to skip the same entries in different instances.
Compare Columns and Avoid Duplicates
Suppose, you need to compare the values in two columns and avoid duplicates. In that case, the given VBA code can be very effective.
- First, right-click on your Sheet name at the bottom > View Code.
- Then, copy-paste these and click Run. Change
A:Bto your column as required in the code.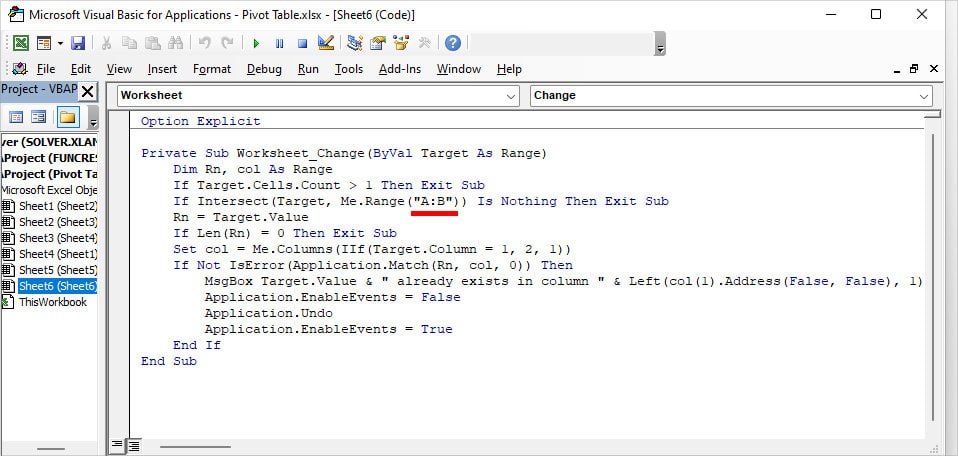
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim Rn, col As Range
If Target.Cells.Count > 1 Then Exit Sub
If Intersect(Target, Me.Range("A:B")) Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
Rn = Target.Value
If Len(Rn) = 0 Then Exit Sub
Set col = Me.Columns(IIf(Target.Column = 1, 2, 1))
If Not IsError(Application.Match(Rn, col, 0)) Then
MsgBox Target.Value & " already exists in column " & Left(col(1).Address(False, False), 1)
Application.EnableEvents = False
Application.Undo
Application.EnableEvents = True
End If
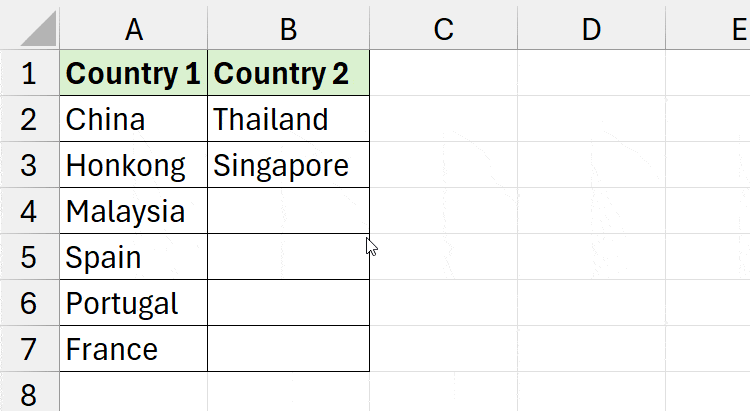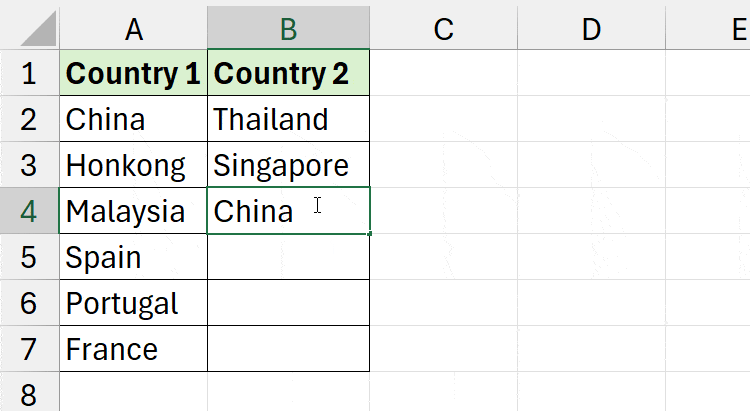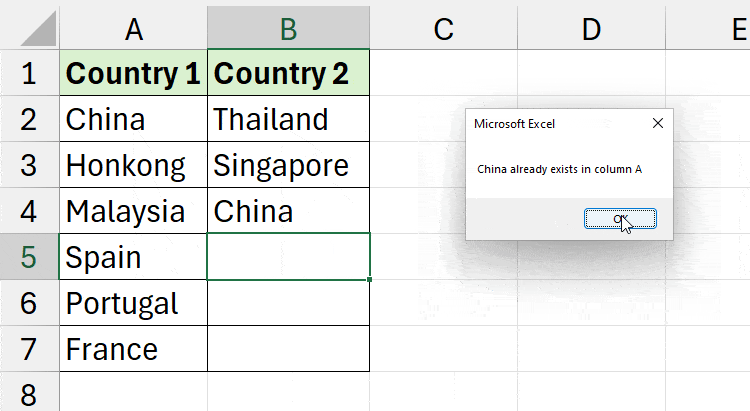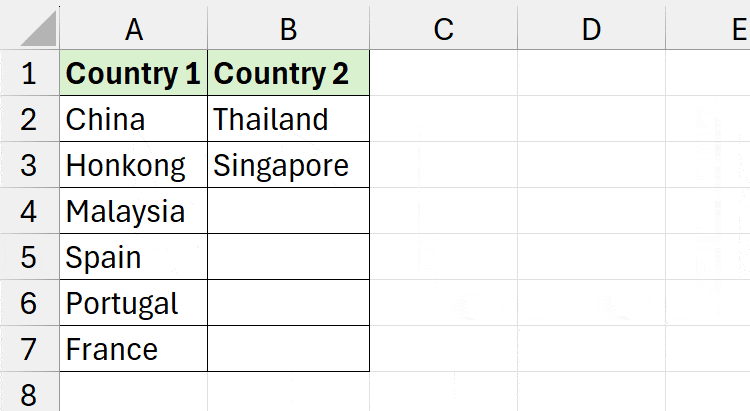
End SubIf I enter the China in Column B that matches with Column A, I’ll receive a “China already exists in Column A message.” It stops me from recording the same item.
Prevent Duplicate Dates
Sometimes, you may want to skip duplicate dates. For that, follow the steps. Make sure there is a Developer Tab in your Ribbon to perform this.
- Use Alt + F11 for the VBA window.
- Expand Insert > Module.
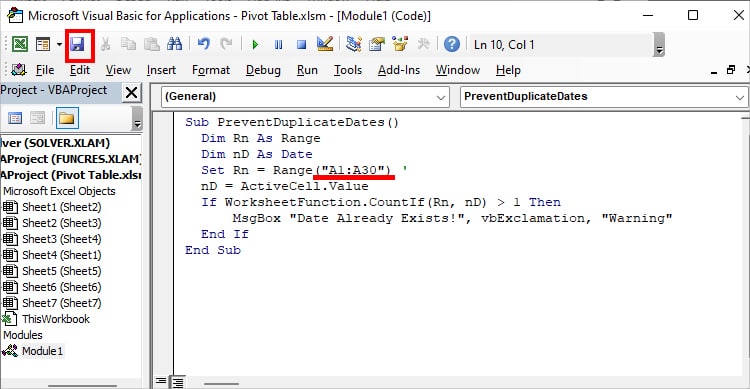
- Copy-Paste the code. Remember to type your cell range in “Enter Column Range” as in the picture.
Sub PreventDuplicateDates()
Dim Rn As Range
Dim nD As Date
Set Rn = Range("Enter Column Range") '
nD = ActiveCell.Value
If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Rn, nD) > 1 Then
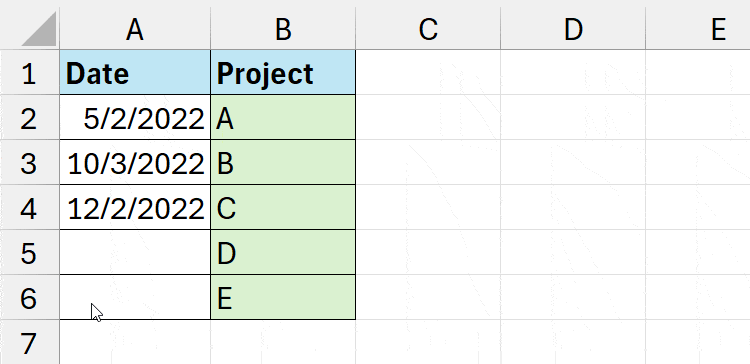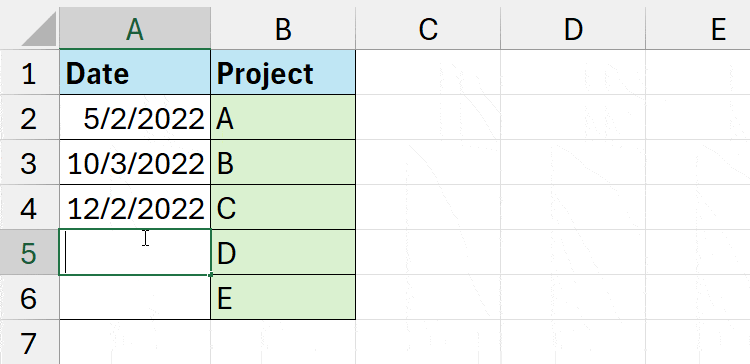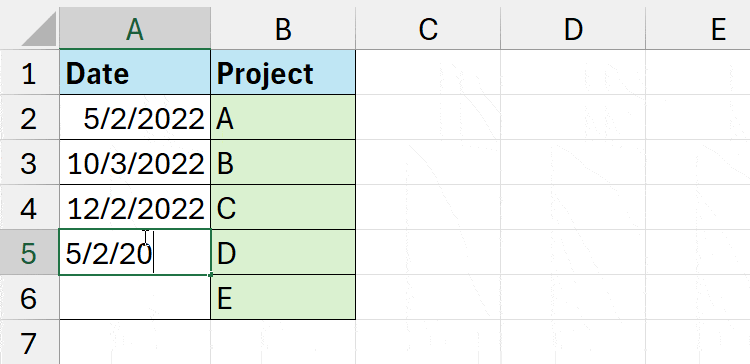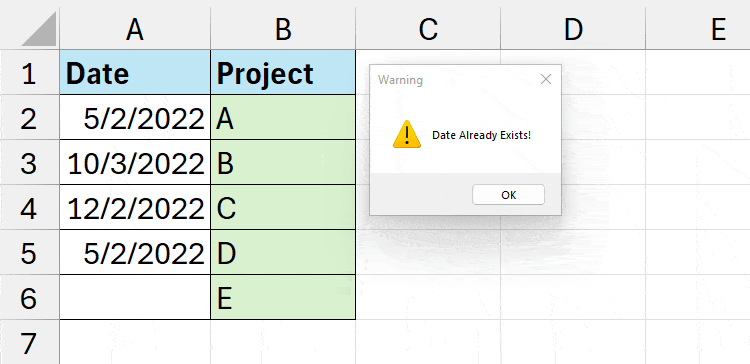
MsgBox "Date Already Exists!", vbExclamation, "Warning"
End If
End Sub
- Click Save. If prompted, you might need to save your workbook as Macro-enabled.
- Now, right-click on Sheet name > View Code.
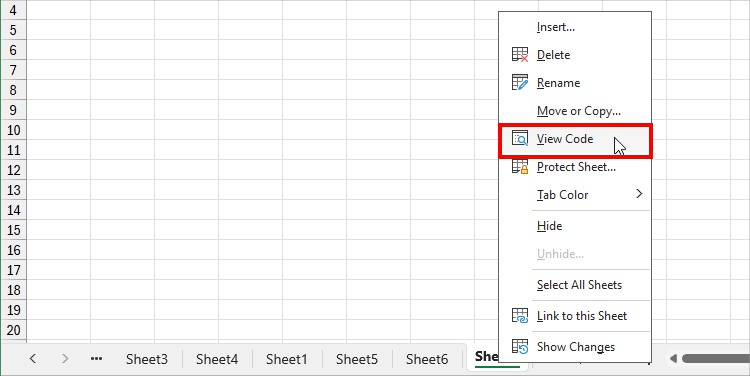
- Copy-paste this. Type your Range in “Enter Column Range” and hit Run.
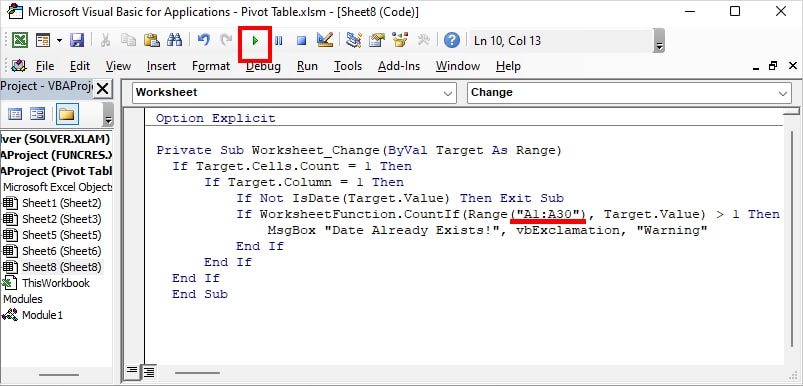
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
If Target.Cells.Count = 1 Then
If Target.Column = 1 Then
If Not IsDate(Target.Value) Then Exit Sub
If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Range("Enter Column Range"), Target.Value) > 1 Then
MsgBox "Date Already Exists!", vbExclamation, "Warning"
End If
End If
End If
End SubYour Sheet is set to detect the duplicate dates. For Instance, if I enter the same date, I’ll receive a Date Already Exists Warning.