Among all other spreadsheet programs, Excel is one of the most popular and quite powerful. But, this does not mean Excel is free from errors and problems.
Sometimes, your Excel app might not respond or could crash abruptly. The app could even freeze for 2-5 minutes without any warning message. Now, this can be a major issue if it occurs repetitively. It can interrupt your workflow and corrupt the workbook.
In most cases, Excel freezes and crashes when the app is used for a long time. Or, if there are other heavy background applications in use. So, before you move on to the major fixes, you can try out the basic troubleshooting steps first.
Force Quit Excel
The first thing you should do when your Excel freezes or is unresponsive is to force quit the app. By this, I do not mean to close the app and restart it again. You need to force the application to completely end the task from the Task Manager. Then, start everything from the beginning.
- On Windows, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys together for the Task Manager window.
- Locate and select Excel from the lists. Then, click End task.
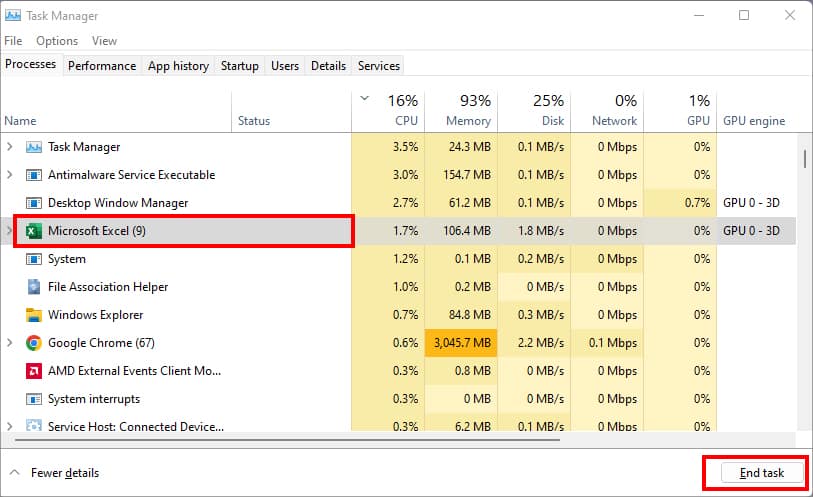
- Close the Task Manager window.
Check and Close Heavy Apps in Use
Are you using heavy applications in the background? Excel itself is a heavy app that excessively uses your device’s RAM especially when your file size is big.
So, if you run other powerful apps like Photoshop, OBS, Antivirus, Games, Web Browsers, etc along with Excel, the app will crash. This happens mostly on PCs with low RAM.
Again, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to go to the Task Manager on Windows. Check if there are other running apps. To close, select the app and hit End Task one by one.
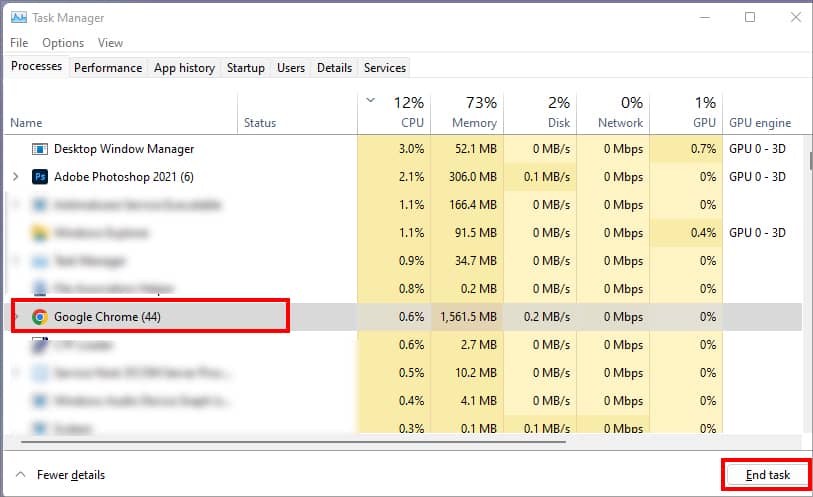
Now, that you have ended the active applications on your device, perform a Quick Restart of your PC. I highly recommend this step, especially for users who put their Devices to sleep overnight. When you do this for a long time, your PC will lag and interrupt the running applications.
Check Excel File Contents and Clean Data
As I have mentioned earlier, the larger your workbook is the more computer RAM Excel uses. This includes hyperlinks, complex formulas, VBA codes, overuse of Conditional Formatting, sheet references, data from external connections, hidden rows and columns, and many more. It can lead to poor performance of the App.
Also, if you have outside links in your workbook, it can cause issues in the workbook. External links can bring malicious malware into your File. As a result, it can cause Excel to crash.
Here’re a few tips to clean up the Excel workbook to reduce the file size. By doing so, Excel will use less memory on your system.
- Remove external links from your data.
- Clear Conditional Formatting. It might sound unusual, but the conditional formatting in your workbook could be corrupted. Comparatively, most users who had excessive conditional formatting reported encountering crashes.
- Unhide Hidden Rows and Columns. If needed, Delete the Hidden rows or columns at once.
- Delete Blank Rows and Columns. Blank cells within the data only expand the spreadsheet size.
- Unfreeze Panes.
- Delete Shapes, Pictures, SmartArt, and Charts from the workbook.
- If needed, clear all formatting at once.
- Try to limit using Volatile Functions – the functions that change the output on each recalculation. For example: NOW, TODAY, RANDBETWEEN, RAND, etc.
Save Large Files as .XLSB Binary Format
Does Excel stop responding when saving huge sheets? If your workbook size is still big even after deleting the unwanted items, you can save the files in .xlsb binary format. In Excel, the Binary Workbook format will decrease the file size. It is also the best file format to send workbooks as an email attachment.
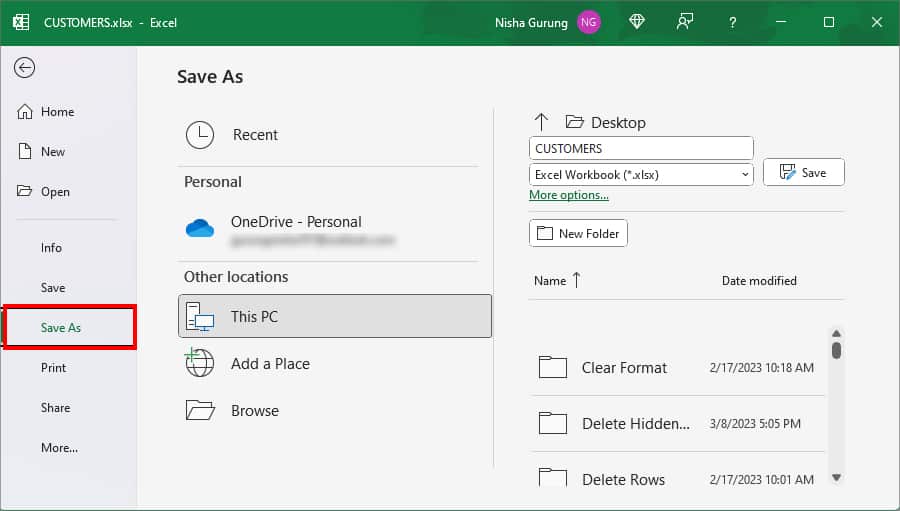
If the issue lies in only one workbook, you can opt for the Save As menu to change the file format.
- On your sheet, click File Tab.
- In the left panel, select Save As.
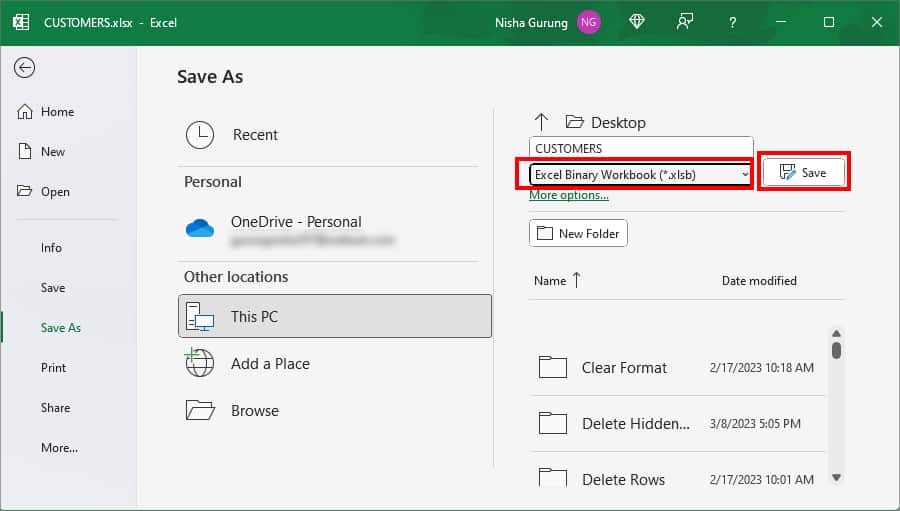
- Below the File name, expand the drop-down menu and pick Excel Binary Workbook (*.xlsb) from the lists. Then, click Save.
Ensure Excel is Not in Use by Another Process
If you attempt to use Excel while the app is already in another process, Excel will crash. During such an instance, you should get the message “Excel is in use by another process” at the status bar. But, you might have failed to notice that message.
If that’s the scenario, you need to wait and allow the process to complete. Once it is done, you’re good to use Excel.
Launch Excel in Safe Mode and Remove Excel Add-Ins
Without a doubt, Add-Ins are a great way to extend Excel’s functionality. But, occasionally, these same Add-Ins can conflict with Excel and lead to app crashes. This is because generally, attackers might use them as a means to harm your device.
If you have installed Add-Ins, you can start Excel in Safe Mode to find out.
Firstly, close the Excel app. Now, hold down the CTRL key. Then, while you’re still pressing that key, click on Excel App to open. Once a Safe Mode confirmation pop-up opens, release key and click Yes to confirm.
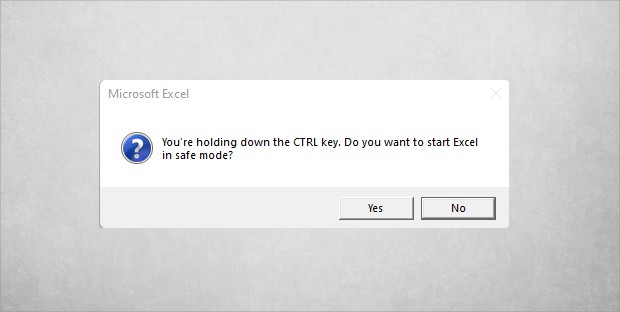
Now, observe the behavior of Excel while opening it in Safe Mode. Does it start normally like usual or are there any issues?
If there are no issues, Add-Ins aren’t the culprit. However, in case you encounter a problem, you need to disable Add-Ins to troubleshoot them.
- On your Excel, click the Options menu.
- On a new window, click Add-ins in the left menu bar.
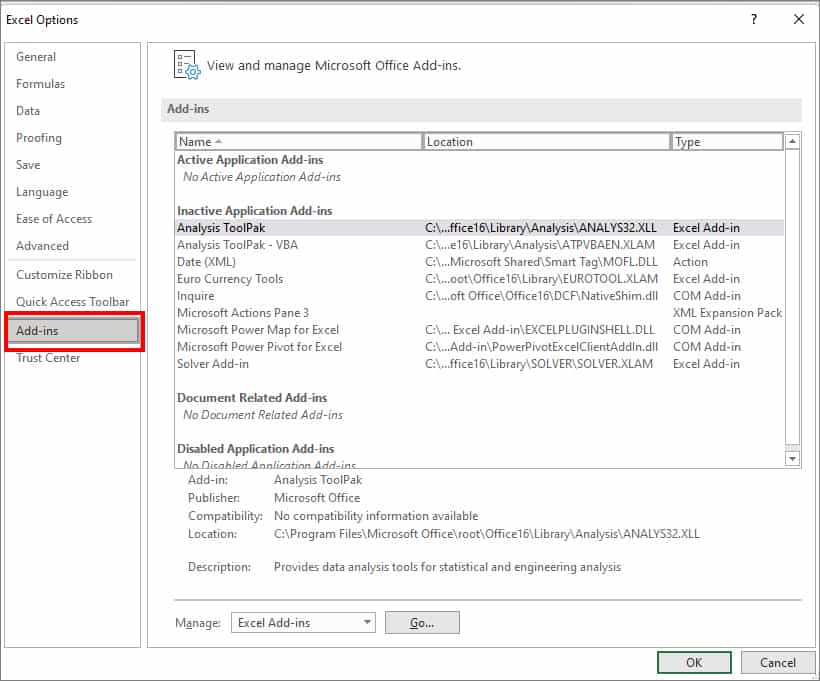
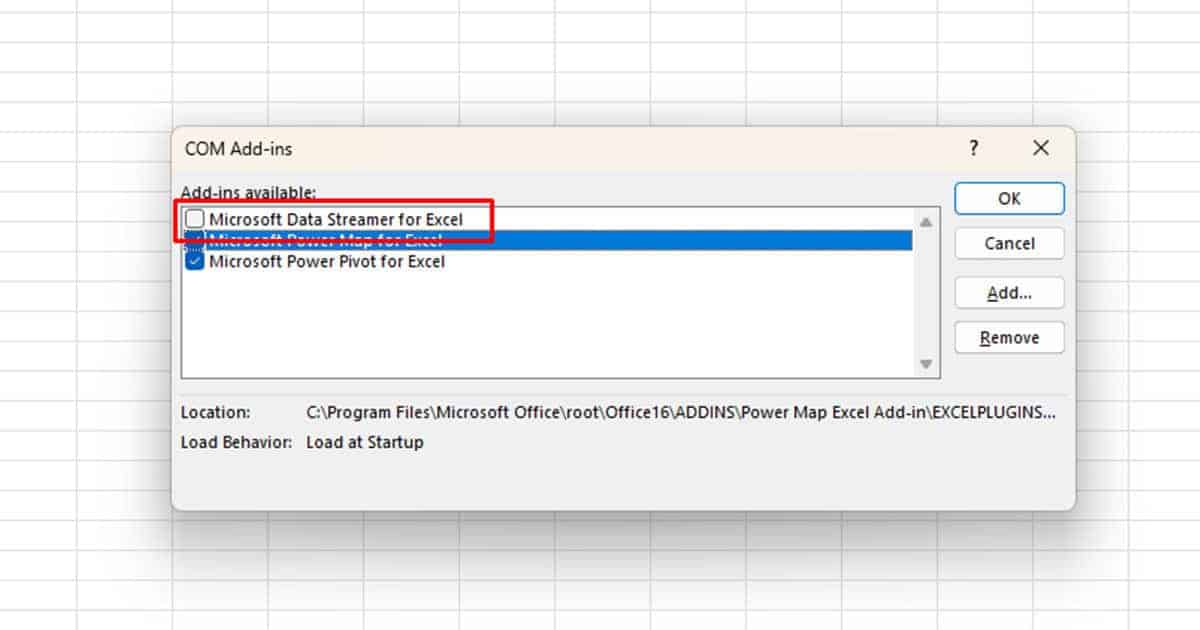
- Next to the Manage menu, expand the drop-down and pick COM Add-ins. Then, click Go.

- On the COM Add-ins dialogue box, tick the boxes for an Add-In to select them. Then, click Remove.
Delete Temp Excel Files
Excel stores unsaved workbooks in the Temp files of your PC so that you can auto-recover the files. It could be during instances like sudden PC shutdown, app crash, or lost internet connection. Although the temp files can come in handy to help recover your files, some of them could be problematic.
Since most users don’t clear the temp files more often, it gets piled up on your device. It’s better to clear them all out.
If you want to recover any files prior to deleting them, copy the files and paste them into another location.
- For the Run command, enter Windows + R key.
- In the Open field, enter
%appdata%\Microsoft\Excel\and hit OK.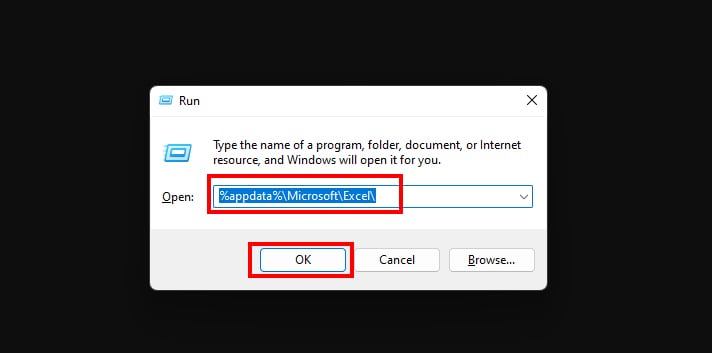
- On the Excel window, you can see the lists of Temp Files. While holding down the Ctrl key, select All files.
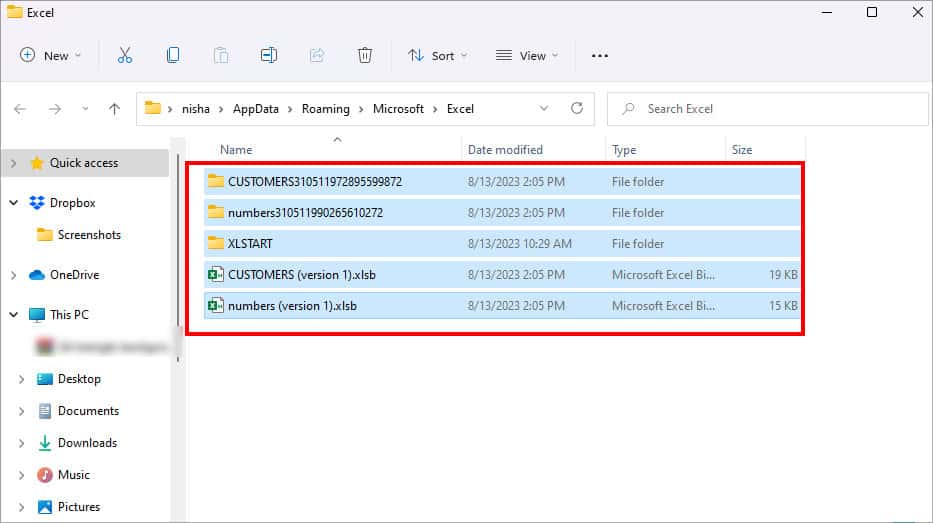
- Right-click on the Files and choose Delete.

Move Workbooks from XLStart Folder
If you have added workbooks or templates in the XLStart Folder, those files will open as soon as you launch Excel. It shouldn’t be a problem with one or two files. But, if there are too many or large files to open, Excel might freeze and crash. To address this, you can relocate the files.
- Open Excel.
- Click Options.
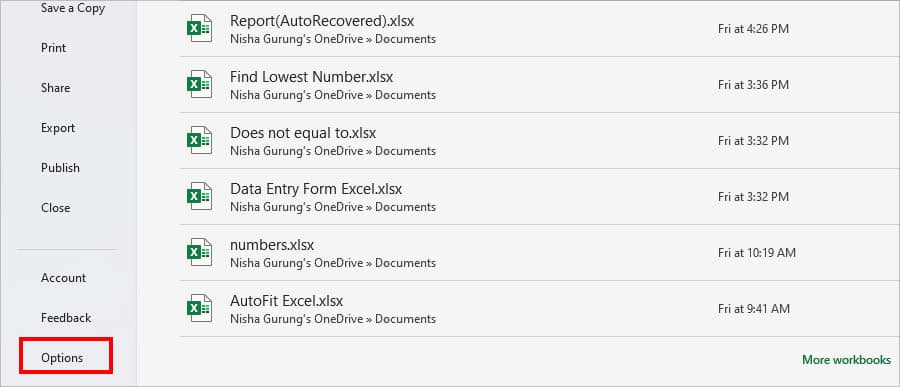
- On the Excel Options window, go to the Trust Center. Then, click Trust Center Settings.
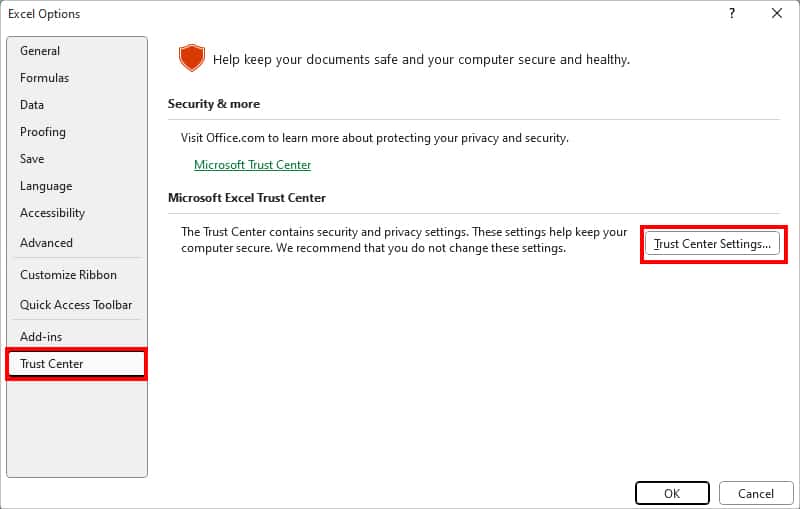
- On the Trust Center window, select Trusted Locations. Under User Locations, see the File Path that has XLSTART in the end.
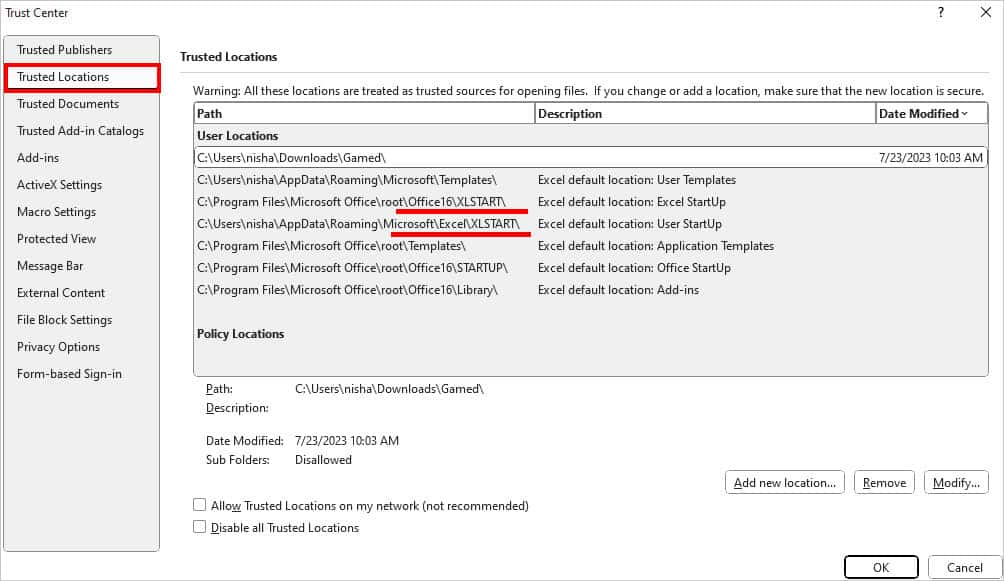
- Select the XLSTART File and click Modify.

- On Microsoft Office Trusted Location, click Browse.
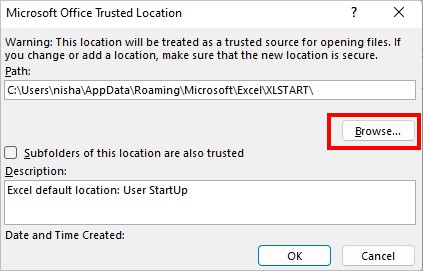
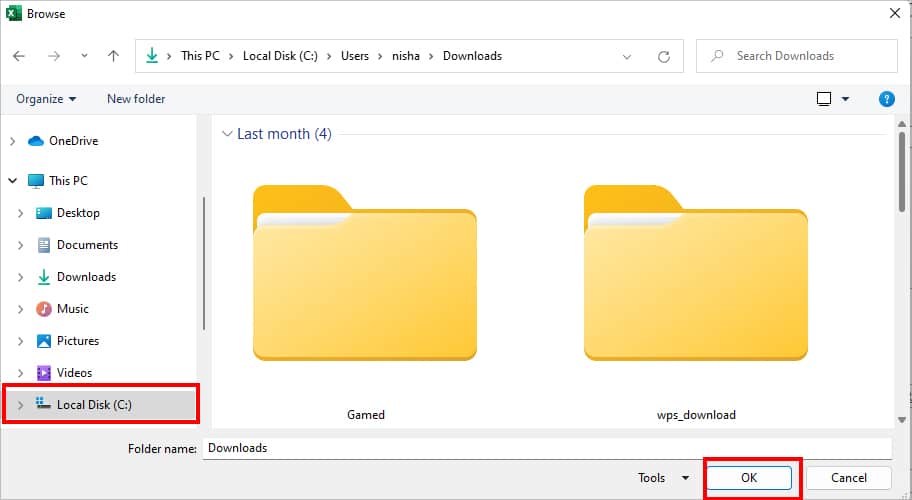
- Now, select a Different location in the Browse Window and click OK.
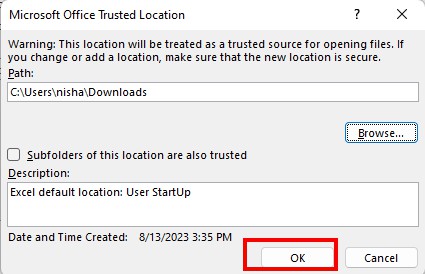
- Again, Click OK.
- Repeat steps 5, 6, and 7 to move other XLSTART files.
- Click OK.

Disable Macros
Although Macros are the best to carry out repeated tasks in Excel, some of them can pose a threat too. This is the main reason why Microsoft Offices disables the Macros by default in Excel. Even if they are enabled, Excel will block the external files containing Macros from running.
However, if you have enabled Macros and unblocked files to run Macro in Excel, it can bring harmful Macro viruses and malicious software that are harmful to your PC. It could be the one causing Excel to crash.
To address this issue, disable Macros in Excel. And don’t worry! There’s an option to Disable Macros with a notification which means you will get a Security Warning Message with Enable Content. So, you can choose to turn on Macros only for the selective files when you want to.
The quickest way to modify the settings is from the Developer Tab. If you don’t have it in the Excel ribbon, you must add them before you start.
- On your Excel workbook, navigate to the Developer Tab.
- In the Code group, click on Macro Security.
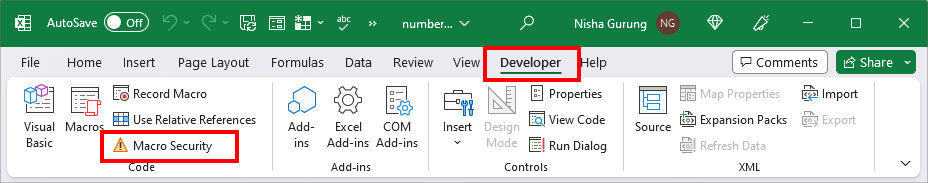
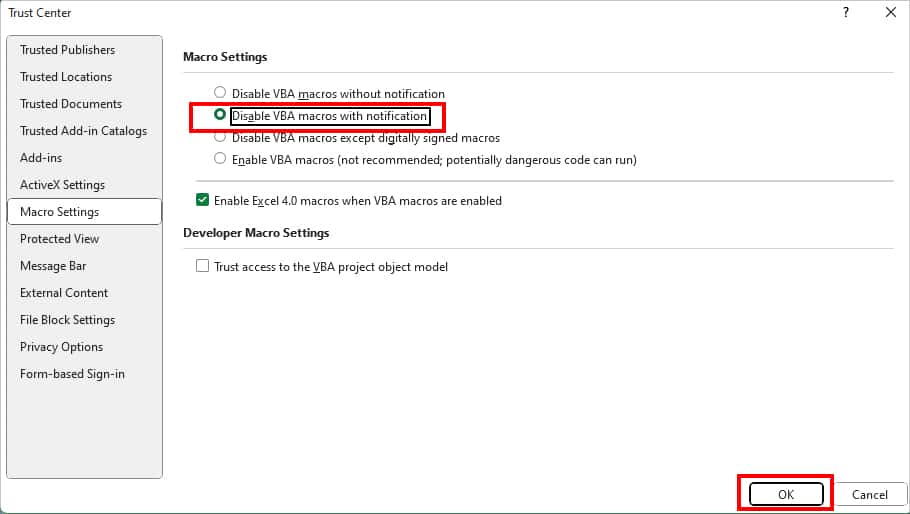
- Under Macro Settings, choose Disable VBA macros with notification and click OK.
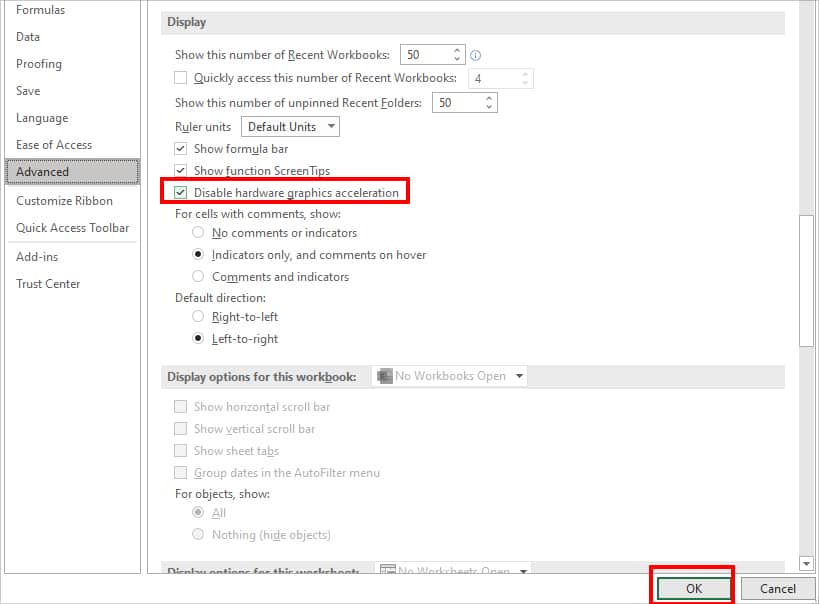
Disable Hardware Graphics Acceleration
In Excel, hardware accelerations are enabled by default to enhance the graphics and animation performance. But, it can also cause screen flickering and not responding issues. To solve this, you can disable Hardware Graphics Acceleration from the Excel Options.
Note that Microsoft 365 versions have not included the Disable hardware graphics acceleration. You cannot turn them off from the Excel Options.
If you use older Excel versions, check out the steps.
- Open Excel.
- Click on Options.
- Go to Advanced.
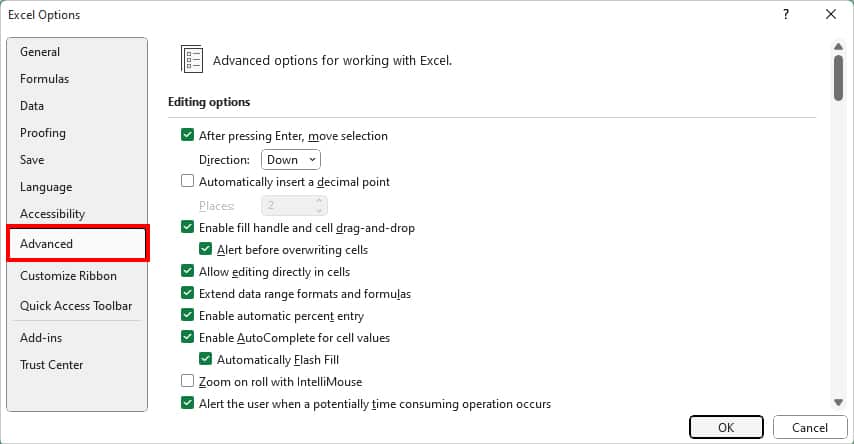
- Locate the Display menu. Tick the box for Disable hardware graphics acceleration and click OK.
Test Excel Features for Third-Party Files
Since Excel has been quite popular among spreadsheets, you can download data in Excel file format from third-party tools too. But, if the file wasn’t created correctly, you might not be able to use Excel features. You could as well encounter issues when opening the files.
The only way to find this out is to check another workbook created in Excel. If you can use the features without any problem, then there’s definitely something wrong with your third-party file.
In that case, you can move the data to a new file. Create an Excel workbook. Copy the information from Third-party Files and paste them into the new worksheet.
Check Antivirus Software
Have you been using Antivirus software on your PC? Antivirus software automatically scans for threats in the background app processes. So, if you attempt to open the corrupt file from third-party tools, it can crash Excel to protect the system. Antivirus won’t allow you to access the file.
Check your System RAM and Office Version
Microsoft Offices offers 64-bit and 32-bit versions for apps. If you have installed the 64-bit versions, your RAM might not be powerful enough to run applications. Insufficient RAM in the PC not only leads to slow performance but also causes Excel to crash. This is the most common problem among users who are using an older PC or the PC with low RAM.
To find out, check the system RAM.
- Head to Window Settings. Simply, press Windows + I.
- Click on System > About.
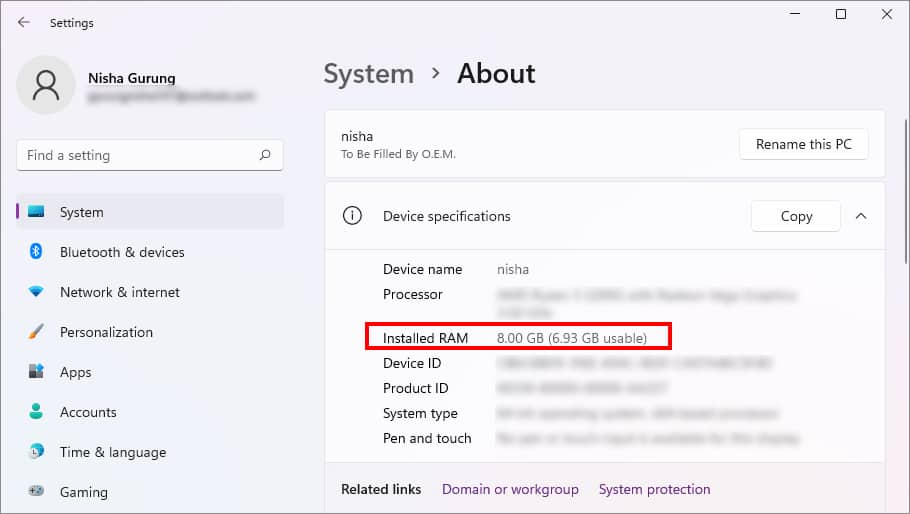
- Below Device Specifications, see the Installed RAM.
Now, to see your Office version,
- Go to Excel and click on Account.
- Select About Excel.
- On the Microsoft Excel window, see the bit version at the top. Once you see, close the window.
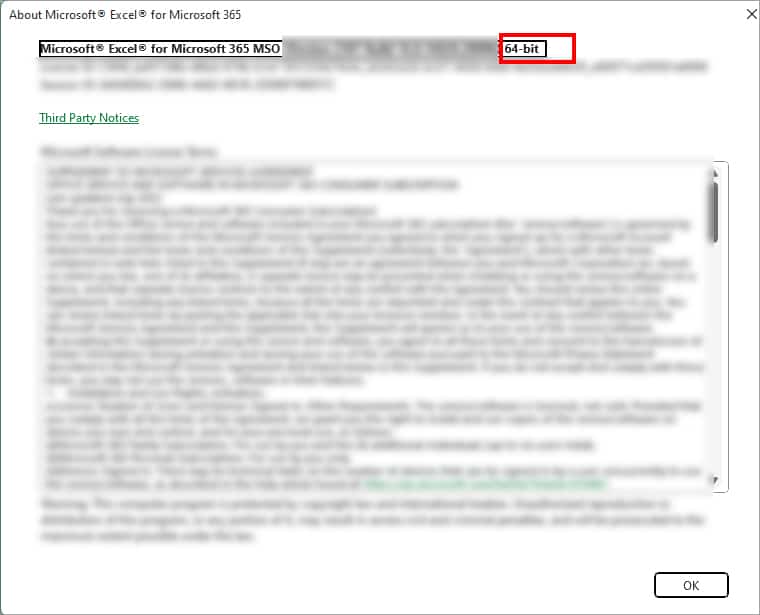
If you have low RAM that might not be enough to run installed 64-bit versions, you can downgrade to the 32-bit version. However, when switching to a lower installer version, you will have limitations. For example, on 32-bit versions, you won’t be able to use Add-Ins installed in the 64-bit version and work with large datasets. So, before you decide, we suggest you go through the Official Site to confirm.
Update Excel
Sometimes, a software bug could also cause Excel to not respond, glitch, or crash. For any errors or bugs, Excel introduces fixes and improvements in the latest update.
- Open Excel.
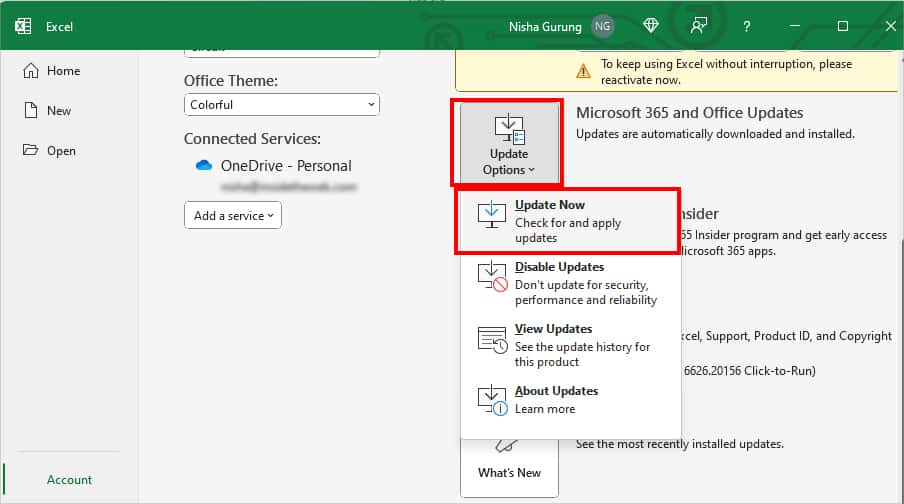
- Go to Account.
- Click Updates. Then, select Update Now.
Repair Office
If there are no updates available, you can perform an Excel Online Repair yourself. Microsoft Repair will scan for any prevailing issues within the Office applications and troubleshoot them. This is the most go-to fix to solve your Excel or any other Office apps not working. It might as well solve the crashing problem.
- For Settings, press the Windows + I keys.
- Click on Apps. Then, go to Installed Apps.
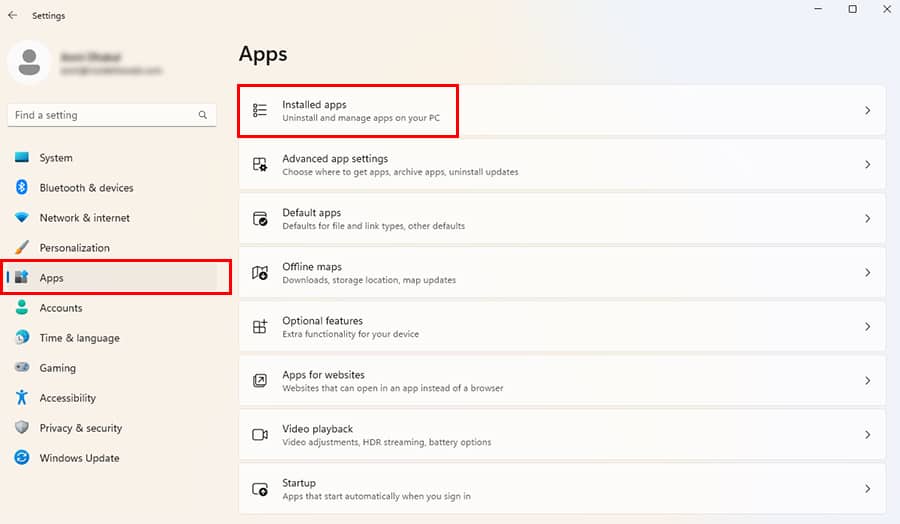
- Scroll to locate Microsoft 365 or Office apps. Click on More Icon > Modify.
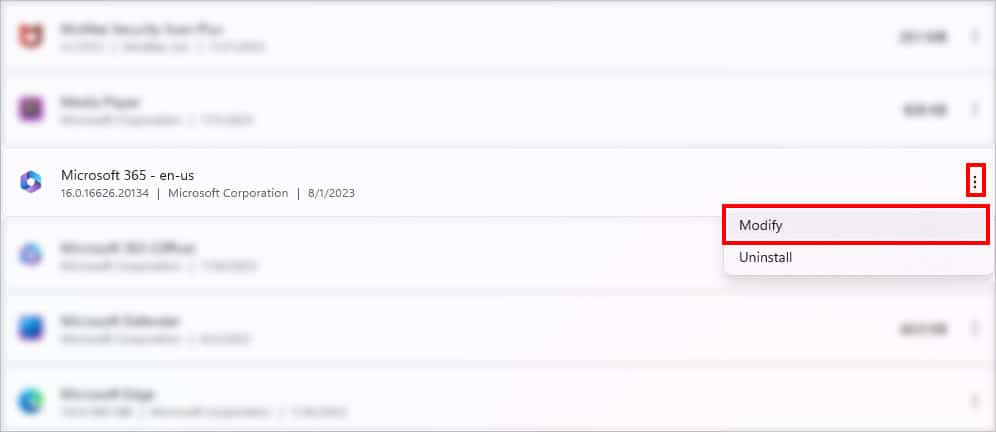
- Hit Yes on the prompt box.
- On the Repair window, choose Online Repair and click on Repair.
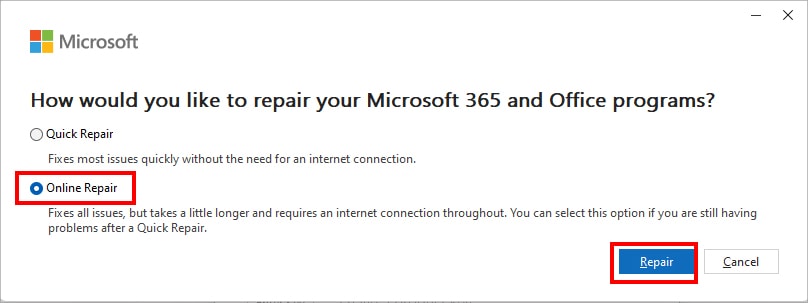
- Restart your PC. Then, open Excel and see if the issue is gone.
Update Device
If the Excel still crashes after the update and repair, maybe the issue could be in your system itself. In that case, update your PC with the latest system software. Then, try using Excel to check if it solved the crashing issues.
- Open Windows Settings (Windows + I) keys.
- Go to Windows Update.
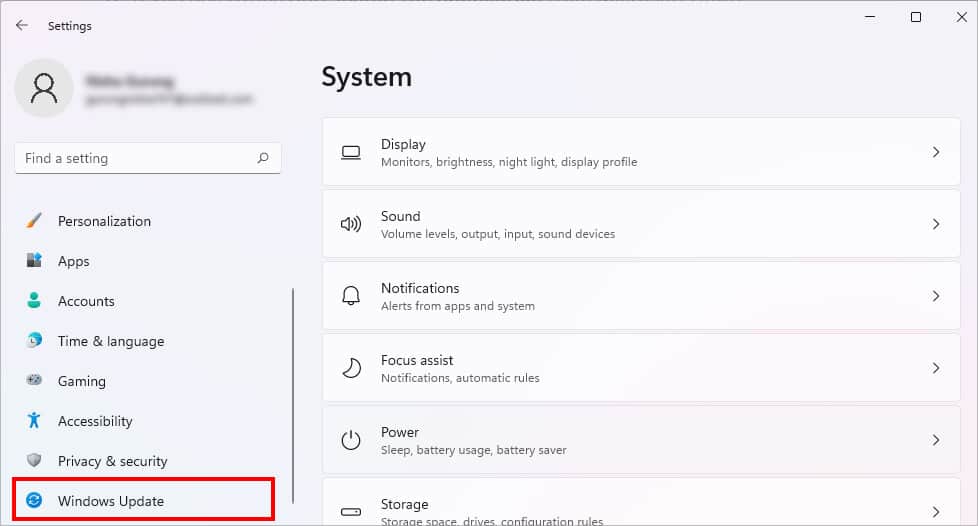
- Click on Download & install. If you cannot find this option, click on Check for Updates. Then, hit on Download & install.
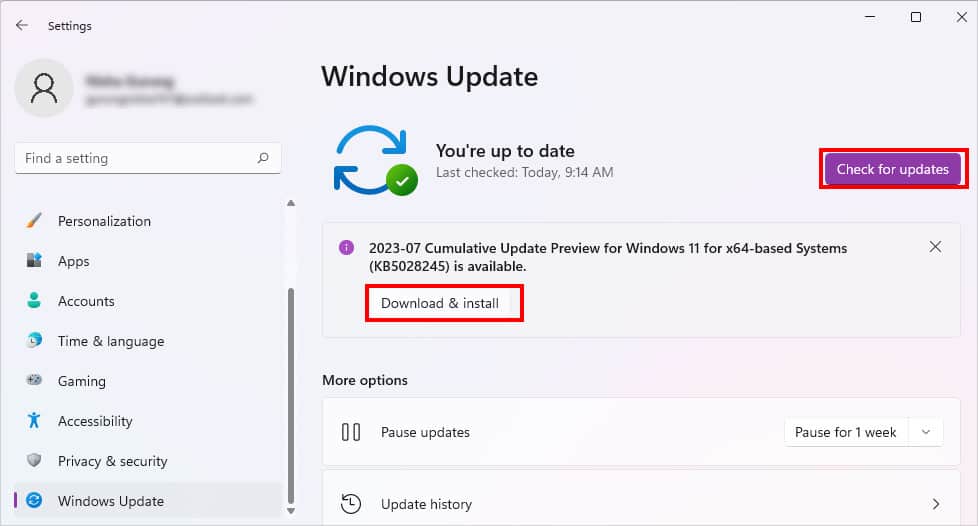
- Restart your PC.
Reinstall Office
It’s better to reinstall Office if Excel still does not respond or crashes frequently. You can uninstall the app. Then, install Office and set up everything from the beginning again.
- Enter the Windows + I shortcut key.
- On the Settings window, navigate to Apps. Choose Installed Apps.
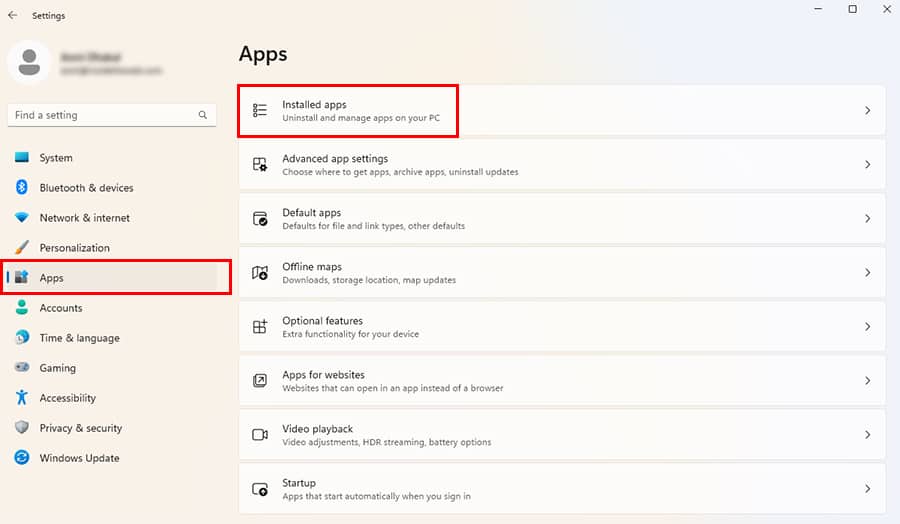
- Find an Office or Microsoft 365 app and click the three-dot icon next to it. Choose Uninstall.
- Pick Uninstall in the prompt box.
- Now, install Office 365 from the Microsoft Store. For older versions, install the .exe file from the official download site.
- Follow the instructions as prompted to set up the application.
Contact Microsoft Office for Help
If the error persists, it’s possible there can be technical issues on Microsoft Office’s site. Your last resort is to contact Microsoft Office Team for help.