Solver is one of Excel’s add-ins built to perform What-If Analysis. Just like Goal Seek, you can determine the input value required to obtain the formula results, but in a more advanced way.
Solver accepts more than one variable cell value. Here, you can specify the objective to return the exact target, minimum, or maximum values. Similarly, you can also add constraints to limit the variables to a particular condition.
For example, you can calculate the estimated sales number and the price of XYZ products in only integers to achieve a profit of 45,000.
You could also use Solver to make critical decisions for businesses based on What-If analysis such as maximizing profits, creating budgets, minimizing company costs, and many more.
How to Insert Solver in Excel?
Solver add-in comes in-built with the Excel app installation. But, you won’t find it in the Data Tab unless you load them to your ribbon. So, check out these steps to insert the Solver add-in to Excel first. However, if you’ve already loaded them, skip this step.
- On your Excel worksheet, go to File Tab.
- Click the Options menu at the bottom.
- On Excel Options, navigate to the Add-ins category. Then, on Manage, ensure you’ve picked Excel Add-ins and click Go.
- Under Add-ins available, tick the box for Solver Add-in and click OK.
How to Use Solver in Excel?
After you’ve added the Solver Add-in, it’ll appear on the Excel’s Data tab. To use Solver, I have split the methods into two steps for more clarity. Basically, you just need to form a model for your problem and input data in Solver.
Here, I have provided an example to find out the variable values for the exact target amount using Solver.
Step 1: Specify the Problem
Firstly, you need to specify the problem that you want Solver add-in to fix for you. It is a very crucial step. When you’re defining a problem, there are three things you should notably point out. Take a look at them first.
Variable Cells: Define a cell or a value you want to change so that it meets your objective.
Constrained Cells: Restrictions or certain conditions for Variable Cells.
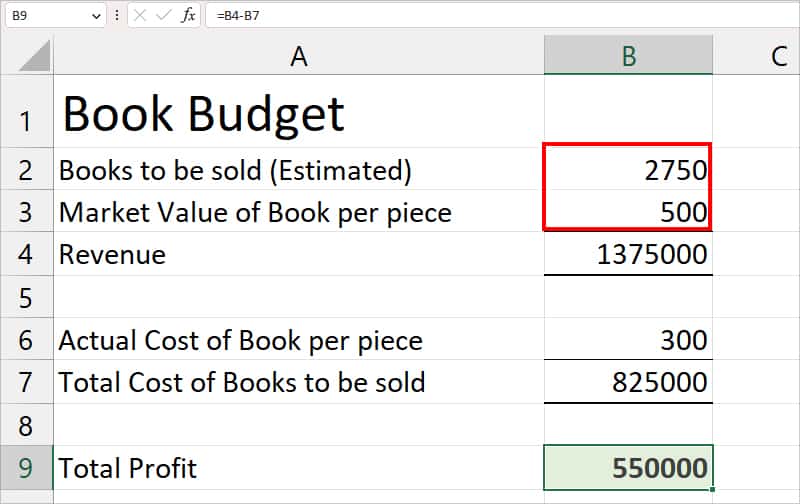
Objective Cells: The Target you wish to achieve in a problem. Your Objective Cells must contain a formula.Scenario: Let’s assume my company is selling books for Client A. According to their price deal, I calculated a profit of 450,000 with the estimated Revenue and Total Costs of Books to be Sold.
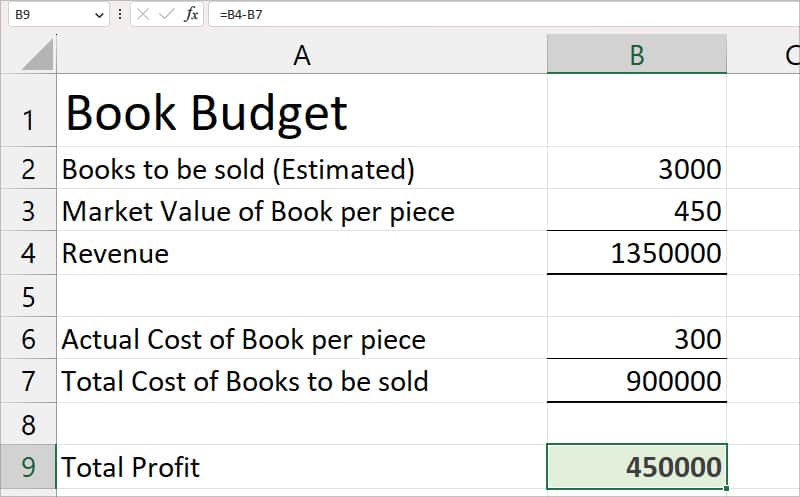
Problem: Now, my client wants to earn a total profit of 5,50,000 from Book Sales. So, I need to find out how many books I must sell and at what price to achieve that goal.
- Objective Cell: $B$9 (Total Profit)
- Variable Cell: $B$2:$B$3 (Since we can’t change the actual cost of the book, we will assign the estimated cost and books for sale to meet the object)
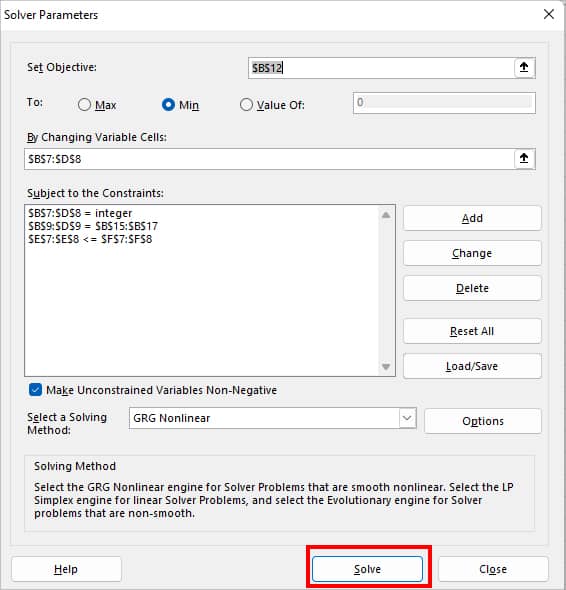
- Constraints: $B$2:$B$3 = integer (It won’t return numbers in decimal value)
Step 2: Use Solver to Fix the Problem
Once we’ve identified the problem, objective, and variable cell, we will input the values in the Solver Parameters box to solve them.
- On your sheet, navigate to Data Tab. Then, in the Analyze section, click Solver.
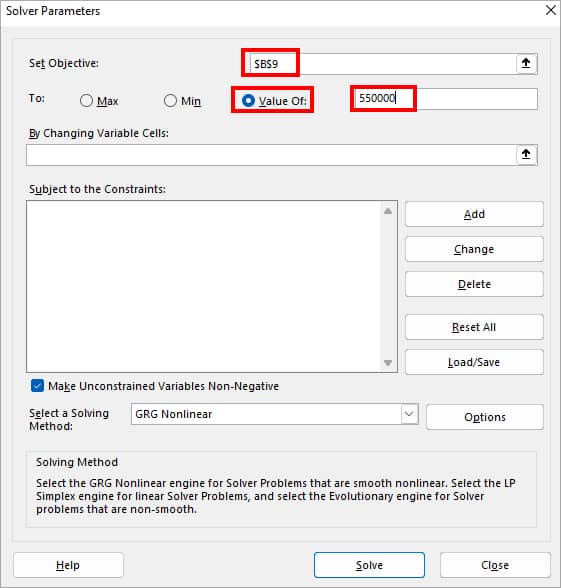
- On the Solver Parameters box, set the Objective first. As shown in the image, my goal is cell $B$9 (Total Profit) set to a Value of 550000.
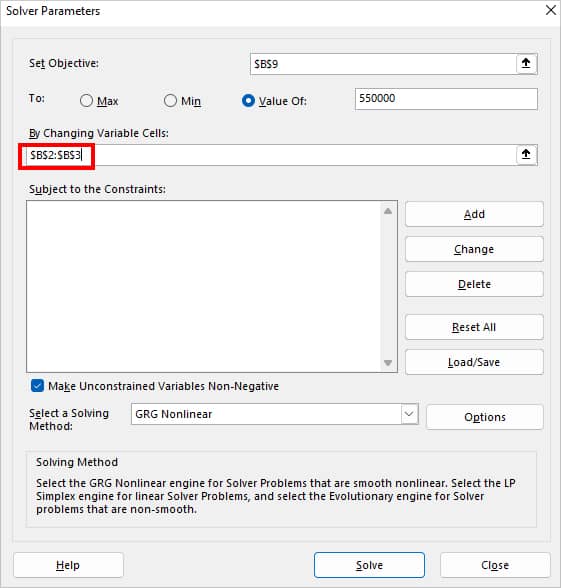
- Now, on By Changing Variable Cells, select Variable Cell references.
- Next to Subject to the Constraints, click Add.
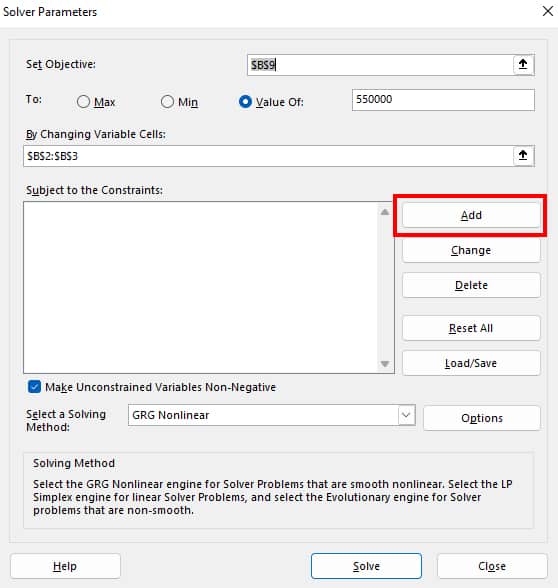
- On Add Constraint window, select Cell Reference and set the Constraint. You can expand the drop-down menu and choose a relationship (<=, =>, =, int, bin, or dif). Here, we set $B$2:$B$3 = integer. When done, click OK.
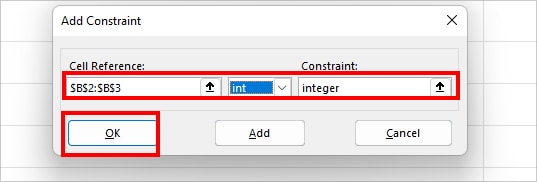
- Hit Solve.
- On the Solver results box, hit OK to confirm.
According to my target, the Solver program changed the estimated books to be sold and the market value of the book price. To gain 550000 profit, I need to sell a total of 2750 books at 500 cost per book.
How to Choose Solver Methods?
If you’ve noticed, the Solver Parameters window has a Select a Solving Method menu. When you expand the drop-down, you can see three options – GRG Nonlinear, Simplex LP, and Evolutionary. These menus are the algorithms that the solver uses to generate answers based on the problems.
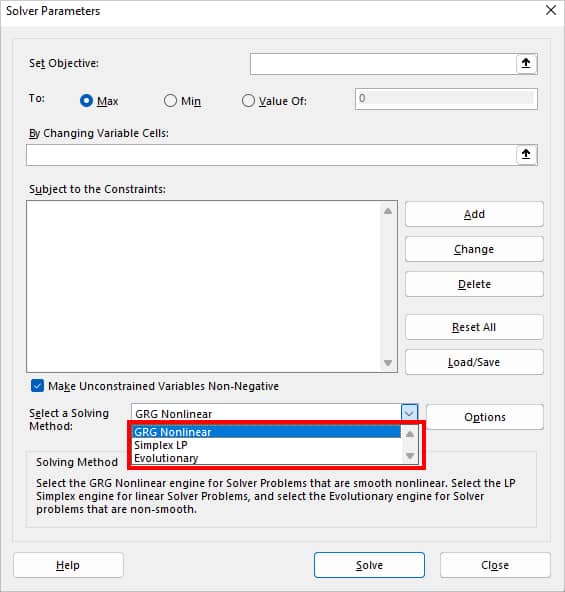
- GRG Nonlinear: Pick this menu to solve nonlinear problems.
- Simplex LP: Choose this method to solve linear problems.
- Evolutionary: Select Evolutionary if you have non-smooth problems.
In case you do not know whether your problem is linear or non-linear, leave the default solver method to GRG Nonlinear as it is.
Other Applications of Solver in Excel
I provided the basic example of using Solver to attain the exact target value above. But, you can also set Maximum and Minimum objectives in Solver for your data. Check out these two examples to learn how to do so.
Example 1: Set Maximum Objective In Solver
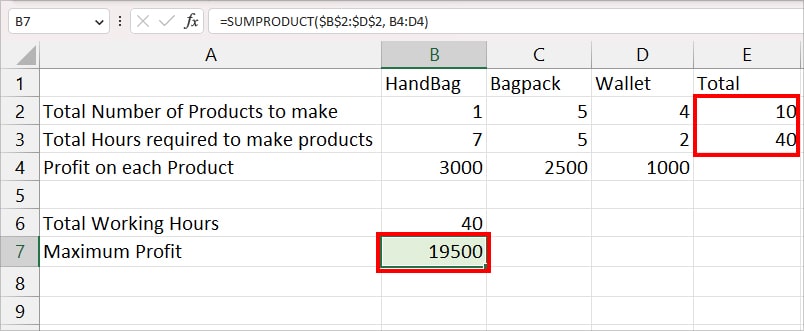
Scenario: I have the data for three products – HandBag, Bagpack, and Wallet. I have the total hours required to make each product and the profit I want to obtain from each product.
Problem: We have total 40 working hours in a week. I need to find out how many number of products I need to make in 40 hours to get the maximum profit.
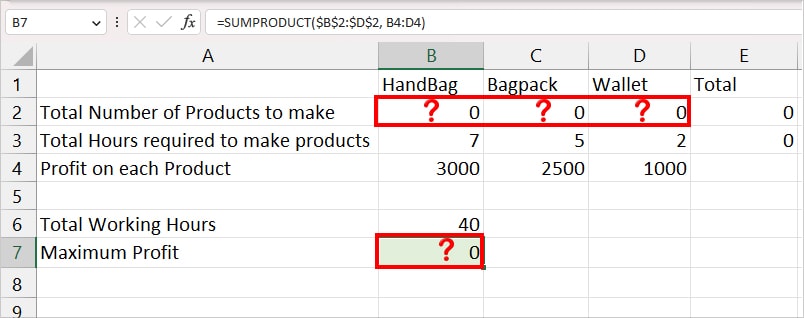
In my case, these are the objective, variable, and constraints for the problem. I suggest you identify these problem models first and note them down as I did. It just makes it so easier to input the value in Solver.
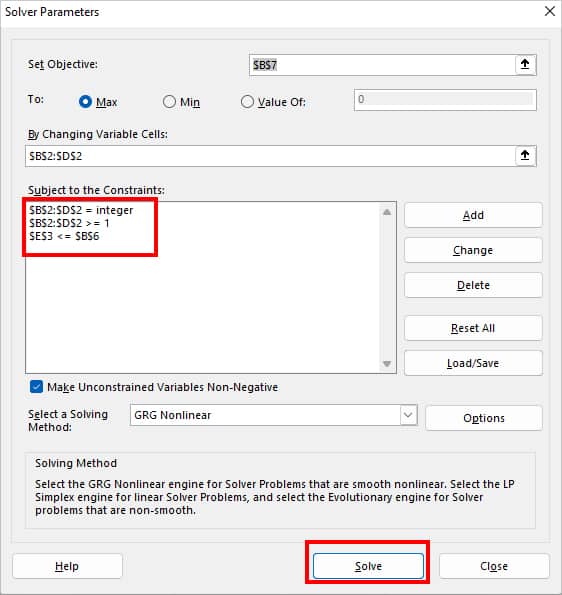
- Objective Cell: $B$7
- Variable Cell: $B$2:$D$2
- Constraint:
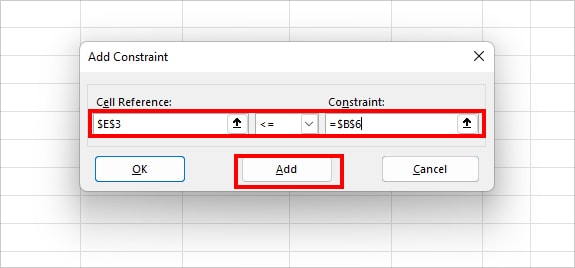
- $E$3<=$B$6 (Total hours required to make product must be less than or equal to 40 hours)
- $B$2:$D$2 = integer (I do not want the value of a total number of products to return in decimal format.)
- $B$2:$D$2 >=1 (Total number of products to make should be greater than one.)
- From Data Tab, select Solver.
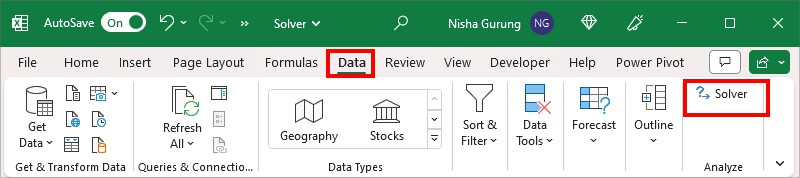
- On Solver Parameters, enter your Cell reference and choose Max. I set the objective for cell $B$7 to Max.
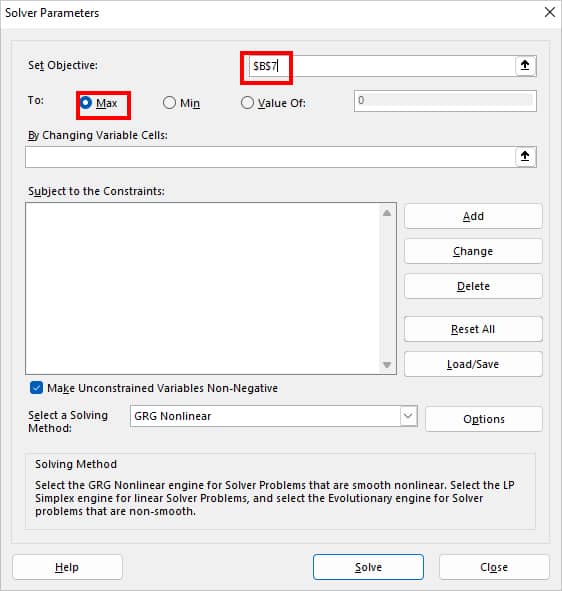
- On By Changing Variable Cells, select the Cell ranges using the Collapse icon. Then, to insert the Subject to the Constraints, click Add.
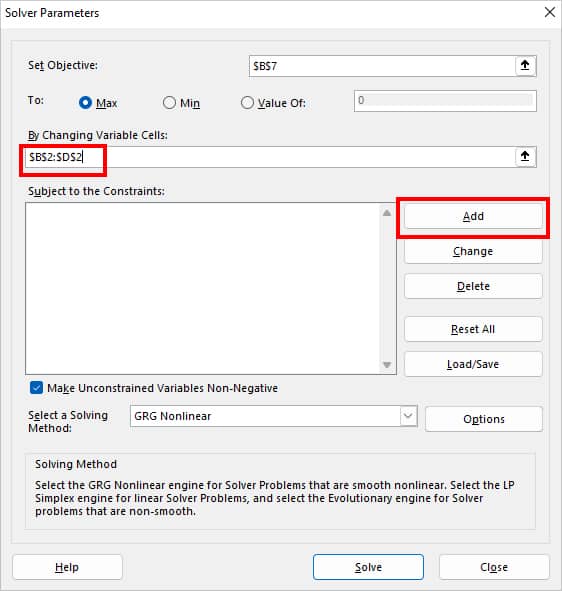
- On Add Constraint, set your Constraint. If you have more constraints, click Add to insert all of them one by one. When done, click OK.
- Finally, hit Solve.
- Click OK to confirm.
According to the Solver tool, we need to produce a total of 10 products in 40 hours to get a maximum profit of 19500 in a week.
Example 2: Set Minimum Objective In Solver
Getting Maximum value is not always the case in the practical business world. For Instance, if you’re handling logistics companies, your primary goal would be to reduce the shipping charge as low as possible to increase profit.
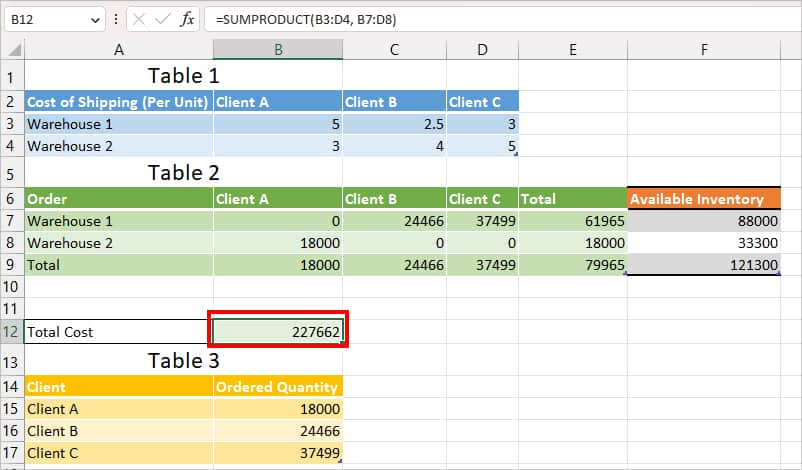
Scenario: My company has two Warehouses: Warehouse 1 and Warehouse 2. From these two warehouses, I need to ship products to Client A, Client B, and Client C. I have the cost of shipping per unit in Table 1 and the client’s order quantity in Table 3.
Problem: I need to calculate how many total orders I must deliver from each warehouse for all clients to get a very minimum shipping cost in Table 2.
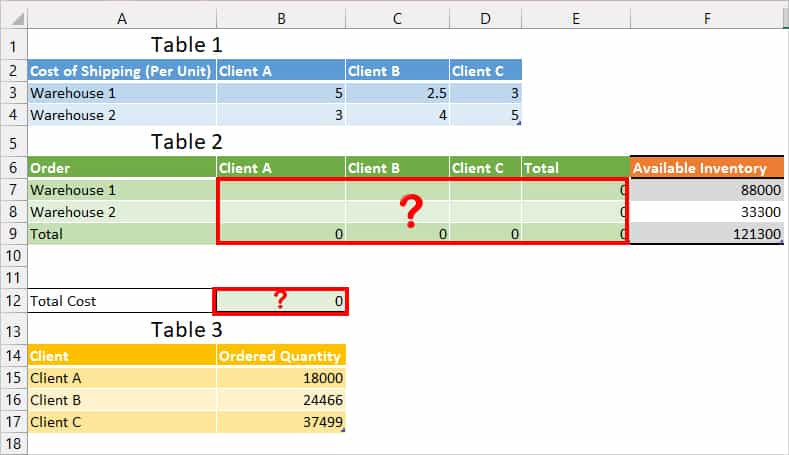
- Objective cell: $B$12 (Total Cost)
- Changing Variable Cell: $B$7:$D$8
- Constraints:
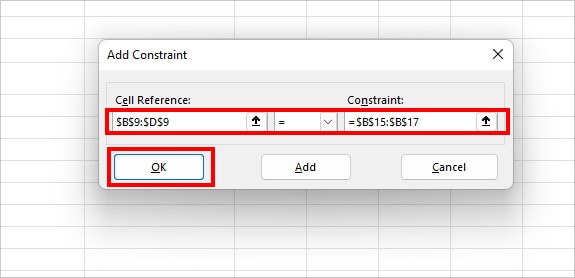
- $B$9:$D$9 = $B$15:$B$17 (The total number you deliver to the client should match their demand)
- $B$7:$D$8 <= $F$7:$F$8 (The number of orders you deliver from each Warehouse should be less than or equal to Available inventory.)
- $B$7:$D$8 int (We want an integer number and not a decimal number)
- On your Data tab, click Solver.
- On Solver Parameters, Set your objective. According to the scenario, my objective is to return Min Value in $B$12.
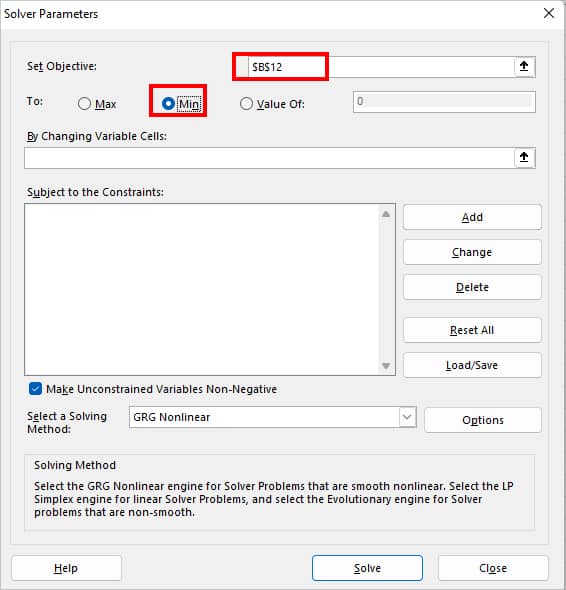
- Select cells for By Changing Variables Cells. For Constraints, click on the Add button.
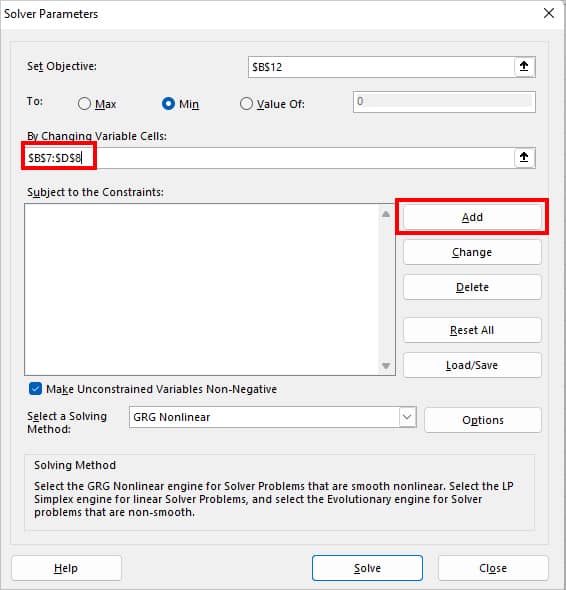
- On Add Constraint box, set your Constraint and click OK. (If you have more constraints, hit Add to insert them)
- Finally, click Solve.
- Hit OK to confirm.
According to the Solver, I need to distribute 61965 orders from Warehouse 1 and 18000 orders from Warehouse 2 to get a low minimum shipping cost .i.e 227662.